Containers and virtual machines
Unix and Linux config :: Containers :: Clusters :: <link>
^ Container Software
A promising starting point, collection of six articles / tutorials on Docker containers:
* https://medium.com/sysf/docker/home
A general note following about three days' Docker container experimentation, and to question "should I be using a Docker container interactively, running multiple apps, some simultaneously?". (Note the following forum post chain is a quagmire of issues and opions!):
* https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=7950326
^ Docker starting point
Notes on Docker containerizing software. Note, to get a practical start it is a good and or needed step to create a user account with Docker dot com. Single user and free accounts with some advanced Docker features disabled are available. A good starting tutorial for beginners is written by one Brian Hogan of Digital Ocean, this article published 2018 July 5. First reference in list here:
Ted noting too there may be a daily limit to the number of docker images which a user with a free account can push to Docker's image repository. Docker's image repository provides URLs of the form https://hub.docker.com/u/<user_name>, where username is the given person's Docker account user name.
^ specific commands
Start a docker image with access to a particular host directory:
-
More on Docker volumes:
^ docker commit ...
^ docker push <image_identifier_string_and_optional_tag>
Series of docker push invocations for a work-in-progress image. Note the tag names are optional until one needs push an image that's being amended, such that it is a newer or different version of an existing image on the remote Docker repository:
886 docker push tedhavelkaad0602/ubuntu-git-plus-arm-none-eabi-gcc 932 docker push tedhavelkaad0602/ubuntu-git-plus-arm-none-eabi-gcc:version-0p2 944 docker push tedhavelkaad0602/ubuntu-git-plus-arm-none-eabi-gcc:version-0p3 962 docker push tedhavelkaad0602/ubuntu-git-plus-arm-none-eabi-gcc:version-0p4 965 docker push tedhavelkaad0602/ubuntu-git-plus-arm-none-eabi-gcc:version-0p5
Delete a Docker repository on Docker hub:
^ docker container rm [...], docker image rm [...]
Delete (remove) a local Docker image . . . first must remove all local containers which use given image:
- https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/container_rm/
- https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/image_rm/
Commands which worked locally:
1036 docker ps -a 1037 docker container rm bdc45e3021ad 1038 docker ps -a 1039 docker container rm 3899ce3b4c5f 85206c6c2565 1040 docker ps -a 1041 docker container rm e530246d9393 775ef655da0f 51a5967aecf8 1042 docker ps -a . . . 1047 docker image rm tedhavelkaad0602/ubuntu-04-vim--openssh-server--man-db 1048 docker images 1049 docker image rm tedhavelkaad0602/ubuntu-nodejs-net-tools 1050 docker images
Secure shell into, or otherwise connect with a running Docker container in and of a Linux environment:
- https://github.com/linuxserver/docker-openssh-server
- https://github.com/linuxserver/docker-openssh-server/blob/71d16e9d09cf8b319ccec9bde2e64ed9298a6d95/LICENSE
A couple examples of running second bash instance of a given Docker container, not a login, but provides second interactive window or interface to a given Docker container:
^ docker exec [options] [command_in_container]
937 docker exec -t -i a42e2e801d60 bash 938 docker exec -i -t 51a5967aecf8 bash
Note this can have unintended consequences given that there's no ssh server running to handle multiple, or additional logins!
-- Enable USB access in Docker container --
^ Docker volumes
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-share-data-between-docker-containers
^ Anatomy of a Dockerfile
Ok Ted needs to figure out what are Dockerfiles and how should they be authored and maintained. One example that's annotated:
A link to a Docker based project which comes very close to what we're working on for an embedded development toolchain and environment that's fully tracked, easy to reproduce on demand:
^ Promising Docker images
^ to access physical devices within container
Notes on how to set up a Docker container registry, a networked server from which Docker images can be accessed and shared:
- https://docs.docker.com/registry/deploying/
- https://docs.docker.com/registry/deploying/#considerations-for-air-gapped-registries
Setting up authentication using htaccess files:
Some requirements for the above link to Docker registry recipe:
Above tutorials and articles don't paint a clear easy path to setting up a first, basic Docker registry. Taking up a different path here at DigitalOcean:
Regarding port forwarding in apache2 config files:
There is some nginx configuration stuff that's not obvious how to port to apache2 config files, but following how-to article gives a clue with "Header set Host ..." and "RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Proto "https"":
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
^ Kubernetes Container Software
Kubernetes notes 2021-06-09 This section a stub section.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
^ Oracle Corporation VirtualBox software
VirtualBox on-line manual
-
Some important VM terms include,
- host OS . . . the OS on which VirtualBox software runs
- guest OS . . . the OS which runs inside a VirtualBox VM instance
- virtual machine . . . the hosting environment which VirtualBox creates for given guest OS
- https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch04.html
- https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch02.html#externalkernelmodules
NOTE! An important BIOS feature and setting to permit virtual machines to run at all using VirtualBox >= 6.1.0 is detailed here at forums dot virtualbox dot org, topic equals 62339:
First set up steps for virtual machine:
To set up shared folders in VirtualBox instances, see VirtualBox documentation chapter 4 at the first following URL. There are also some needed steps detailed in same Oracle documentation, chapter 2, second URL here:
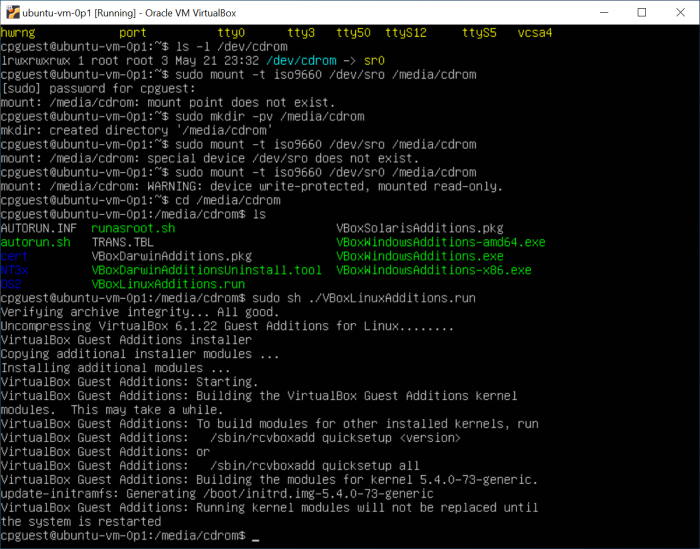
Following screen capture is from Ted's work setting up virtual Ubuntu host.
Figure 1 - capture of VM Ubuntu guest OS command prompt, with steps to mount VirtualBox CDROM drive:
Interestingly, mounting the device /dev/sr0 within the guest OS provides access to several files which we did not see or explicitly install when installing VirtualBox framework software. Scripts to set up needed Linux kernel modules are among these files at /media/cdrom.
To configure port forwarding, for ssh from host OS to guest OS:
Where VirtualBox stores its files . . .
VirtualBox needs a one-time set up for each host OS folder or directory to be shareable with a given virtual machine. Once that sharing configuration is completed, a *nix mount command is needed in a login session in the virtual machine. Example mount commands to make a host OS directory accessible to the given running VM:
Figure x - share files in one directory between host OS and VM:
804 sudo mount -t vboxsf host_os_downloads /mnt/host_os_downloads/
^ ssh to VM on remote Windows station
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
^ References and Notes
For Ubuntu installs be sure to make /boot large enough, e.g. ~500MB when creating a separate /boot partition:
On first use of Docker
Just after installing docker-ce, `sudo systemctl status docker` returns:
● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2021-06-16 18:57:15 UTC; 54s ago
TriggeredBy: ● docker.socket
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
Main PID: 20113 (dockerd)
Tasks: 8
Memory: 40.2M
CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service
└─20113 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
Jun 16 18:57:15 ubuntu-vm dockerd[20113]: time="2021-06-16T18:57:15.411564912Z" level=warning msg="Your kernel does not support CPU realtime scheduler"
Jun 16 18:57:15 ubuntu-vm dockerd[20113]: time="2021-06-16T18:57:15.411704850Z" level=warning msg="Your kernel does not support cgroup blkio weight"
Jun 16 18:57:15 ubuntu-vm dockerd[20113]: time="2021-06-16T18:57:15.411837721Z" level=warning msg="Your kernel does not support cgroup blkio weight_device"
Jun 16 18:57:15 ubuntu-vm dockerd[20113]: time="2021-06-16T18:57:15.412338475Z" level=info msg="Loading containers: start."
Jun 16 18:57:15 ubuntu-vm dockerd[20113]: time="2021-06-16T18:57:15.573219785Z" level=info msg="Default bridge (docker0) is assigned with an IP address 172.17.0.0/16. Daemon option --bip>
Jun 16 18:57:15 ubuntu-vm dockerd[20113]: time="2021-06-16T18:57:15.675938542Z" level=info msg="Loading containers: done."
Jun 16 18:57:15 ubuntu-vm dockerd[20113]: time="2021-06-16T18:57:15.714086036Z" level=info msg="Docker daemon" commit=b0f5bc3 graphdriver(s)=overlay2 version=20.10.7
Jun 16 18:57:15 ubuntu-vm dockerd[20113]: time="2021-06-16T18:57:15.715744202Z" level=info msg="Daemon has completed initialization"
Jun 16 18:57:15 ubuntu-vm systemd[1]: Started Docker Application Container Engine.
Jun 16 18:57:15 ubuntu-vm dockerd[20113]: time="2021-06-16T18:57:15.837838160Z" level=info msg="API listen on /run/docker.sock"
Ted noting this due to the three warnings regarding "kernel does not support x...".
Git client config in VM and Docker container
For firmware dev work whether in virtual machines and or Docker containers, we need access to remote git repositories. SSL keys are necessary for this access. Here are some beginning notes to explain setting up such keys within each environment:
337 ssh-keygen -t ed25519 <-- generate elliptic type key 338 cd .ssh 340 ls -l 341 cat id_ed25519.pub <-- dump public key to terminal to copy 342 which ssh-agent <-- check that `ssh-agent` is installed and in local $PATH variable 346 ps ax | grep ssh-agent <-- check whether ssh-agent is presently running 348 eval `ssh-agent -s` <-- start ssh-agent running when not found running 349 ps ax | grep ssh-agent <-- confirm running in background as a daemon 350 ssh-add ./id_ed25519 <-- add the private key of the public + private key pair created above
GNU Arm Toolchain refs:
- https://developer.arm.com/tools-and-software/open-source-software/developer-tools/gnu-toolchain/gnu-rm
- https://developer.arm.com/tools-and-software/open-source-software/developer-tools/gnu-toolchain/gnu-rm/downloads
gcc-arm-none-eabi-10-2020-q4-major-x86_64-linux.tar.bz2
Linux x86_64 Tarball
MD5: 8312c4c91799885f222f663fc81f9a31
gcc-arm-none-eabi-10-2020-q4-major-src.tar.bz2
Source Tarball
MD5: 0cc79529934703e16ec25a8915028897
On WSL...