Difference between revisions of "Containers and virtual machines"
m (add note regarding Ubuntu 20.04 and near releases /boot min size ~500MB.) |
m (→^ Container Software: Docker, start with access to host OS files.) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
Ted noting too there may be a daily limit to the number of docker images which a user with a free account can push to Docker's image repository. Docker's image repository provides URLs of the form <code>https://hub.docker.com/u/<user_name></code>, where username is the given person's Docker account user name. | Ted noting too there may be a daily limit to the number of docker images which a user with a free account can push to Docker's image repository. Docker's image repository provides URLs of the form <code>https://hub.docker.com/u/<user_name></code>, where username is the given person's Docker account user name. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Start a docker image with access to a particular host directory: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * https://stackoverflow.com/questions/55104551/how-to-access-files-in-host-from-a-docker-container | ||
<!-- comment --> | <!-- comment --> | ||
Revision as of 18:43, 8 June 2021
Unix and Linux config :: Containers :: Clusters :: <link>
^ Container Software
Notes on Docker containerizing software. Note, to get a practical start it is a good and or needed step to create a user account with Docker dot com. Single user and free accounts with some advanced Docker features disabled are available. A good starting tutorial for beginners is written by one Brian Hogan of Digital Ocean, this article published 2018 July 5. First reference in list here:
Ted noting too there may be a daily limit to the number of docker images which a user with a free account can push to Docker's image repository. Docker's image repository provides URLs of the form https://hub.docker.com/u/<user_name>, where username is the given person's Docker account user name.
Start a docker image with access to a particular host directory:
Containers, Kubernetes . . .
Not a container per se but a virtual machine software:
^ Oracle Corporation VirtualBox software
VirtualBox on-line manual
-
Some important VM terms include,
- host OS . . . the OS on which VirtualBox software runs
- guest OS . . . the OS which runs inside a VirtualBox VM instance
- virtual machine . . . the hosting environment which VirtualBox creates for given guest OS
- https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch04.html
- https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch02.html#externalkernelmodules
To set up shared folders in VirtualBox instances, see VirtualBox documentation chapter 4 at the first following URL. There are also some needed steps detailed in same Oracle documentation, chapter 2, second URL here:
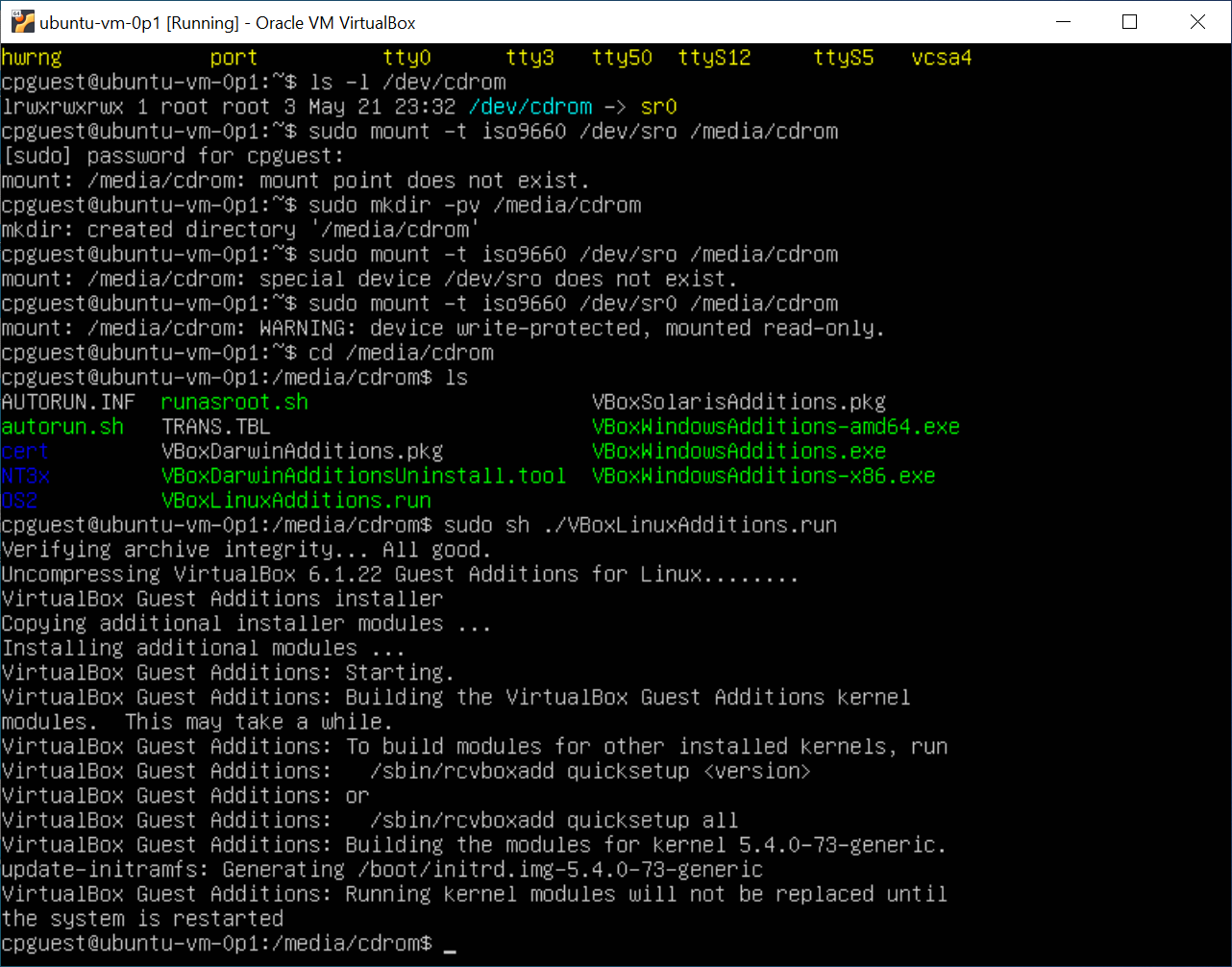
Following screen capture is from Ted's work setting up virtual Ubuntu host.
Figure 1 - capture of VM Ubuntu guest OS command prompt, with steps to mount VirtualBox CDROM drive:
Interestingly, mounting the device /dev/sr0 within the guest OS provides access to several files which we did not see or explicitly install when installing VirtualBox framework software. Scripts to set up needed Linux kernel modules are among these files at /media/cdrom.
To configure port forwarding, for ssh from host OS to guest OS:
Where VirtualBox stores its files . . .
^ References
For Ubuntu installs be sure to make /boot large enough, e.g. ~500MB when creating a separate /boot partition: